Graph-based
Graph-based Asynchronous Event Processing
1. Introduction
-
Since the output of an event camera is a sparse asynchronous events stream, most works transform events stream into:
- regular 2D event frames
- 3D voxel grids
丢失了事件的稀疏性、把事件的时间戳量化
Event-by-event processint:
- SNN
- Time-surface-based methods
对调参敏感、难以训练
-
当前基于事件的GNN仍然是分批处理事件,at the cost of discarding the low latency nature of events data.
-
Contributions
- graph-based recursive algorithm
- a novel incremental graph convolution
- an event-specific radius search algorithm
- 减少了query和insertion/deletion的时间复杂度
3. Method
3.1 Event Graph
-
connectivity of nodes: radius-neighborhood graph strategy
and are connected with an edge only if their weighted Euclidean distance less than R.
-
limit the size of graph: 每个节点有最大度限制
3.2 Spatial Graph Convolution
-
Spatial Graph Convolution
Formally, it aggregates a new feature vector for each vertex using its neighborhood information weighted by a trainable kernel function.
Eq 1.use summation as the aggregation operation - is a function determining how the features are aggregated by making use of two node features and edge attributes.
- is the node features.
4. Method
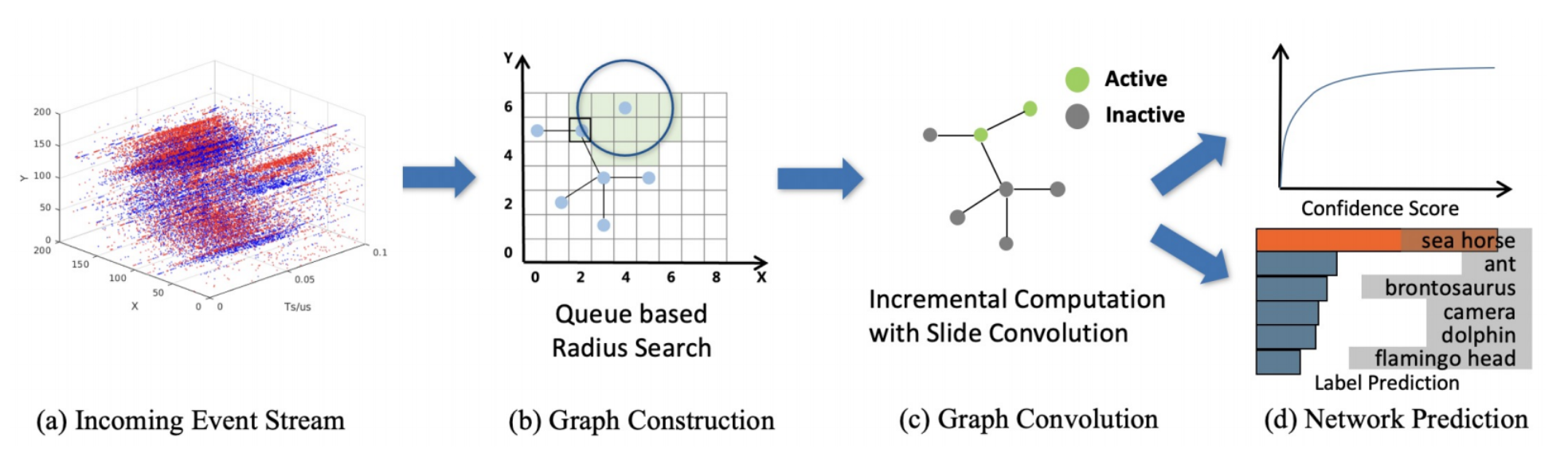
4.1 Slide Convolution
Infeasible version
update the graph by sliding new events in and sliding events out, then apply convolution on the full graph.
- 需要每次移动滑动窗口都处理整个窗口内的事件
Improved version
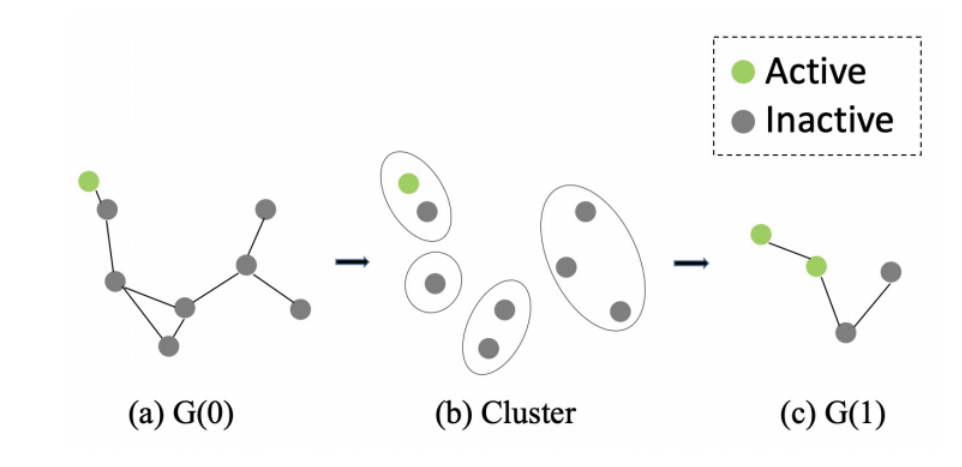
just compute the features around the newly active or inactive nodes.
- 但是仅能应用在单层上
slide convolution
-
rewrite the convolution in a multi-layer architecture
-
: existing set, represents all existing nodes in the graph at layer at n+1
-
: map that stores which nodes at layer n contribute to node i at layer .
Here, is one-hop neighbour of node i.
-
-
leverage the temporal sparsity of the event stream, i.e., some nodes stay same values at 2 consecutive timestamp:
- : a set of directed edges containing all the edges that point to modified nodes.
-
divide nodes that need to be updated into 3 categories:
- the ones deleted from the graph,
- the ones newly added to the graph
- the ones that locate in the receptive field

-
and is built from state at previous layer, 所以不需要记录之前的状态,依次更新过来就行。
-
但是需要维护A的之前状态
-
如何更新?
- for , assigned to zeros
- for , assigned to zeros
-
To extend to pooling operations
: the nodes located in the same voxel()
4.2 Pixel Queue
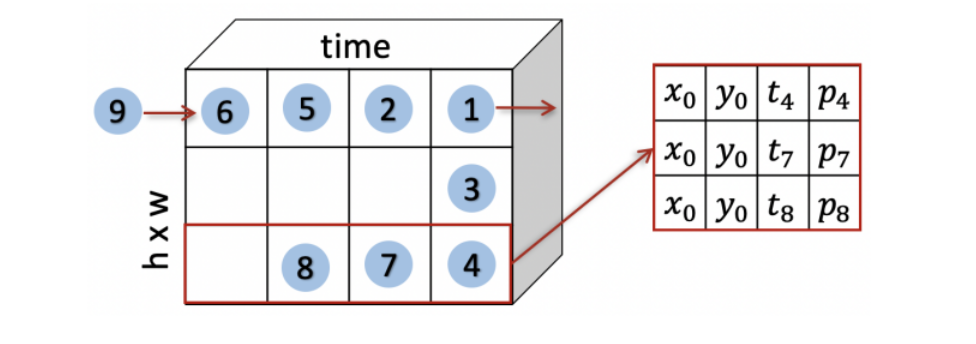
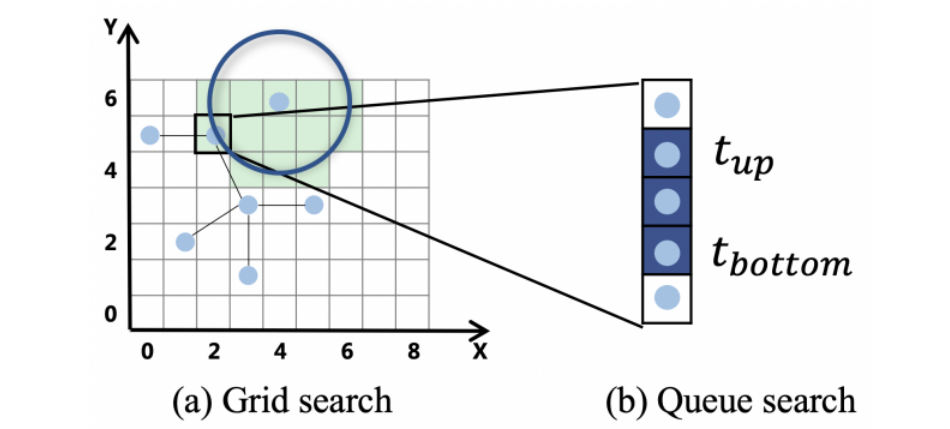
- Pixel queue stores the most recent events at each location sorted by the time of their arrival.
- two-stage radius
- For a query event()and the radius R, we can determine candidate pixels and corresponding queues.
- For a candidate pixel queue with spatial offset from the query event, the target evetns contained in it must have lower bound and upper bound
- 对于上下界,使用二分查找找到位于其中的事件——final query result
4.3 State-aware Module
随着事件增多,预测的结果将会逐渐变得稳定,此时没有必要继续增加更多的事件。
State-aware Module
Specifically, we use a multi-layer perceptron to represent a state-aware function which maps the graph feature map to a binary prediction.
The prediction result means whether it achieves the stable status.
在训练阶段训练MLP, 看作是事件下标的一个函数,当没有明显增加的时候认为达到稳定状态, i.e.输出1.
5. Experiment
-
Comparison to the batch-wise way
减小batch size 减小了延迟但是会导致准确率下降
-
Trade-off between latency and computational effort
Event-wise减小了latency,但是使得计算成本增加。

